प्रश्न 1-ओम का नियम लिखिए ? इसके सत्यापन के लिए आवश्यक प्रयोग का वर्णन परिपथ-आरेख बनाकर समझाइए |
Write Ohm’s law? Describe the experiment required for its verification and explain it by making a circuit diagram.
उत्तर- ओम का नियम — ओम के नियम के अनुसार, “यदि किसी चालक की भौतिक अवस्थाएँ (जैसे चालक के पदार्थ का ताप आदि) अपरिवर्तित रहें तो चालक में बहने वाली धारा, चालक के सिरों के विभवान्तर के अनुक्रमानुपाती होती है।”
यदि किसी चालक के सिरों पर लगा विभवान्तर V तथा उसमें बहने वाली धारा I हो, तब
V/R = नियतांक
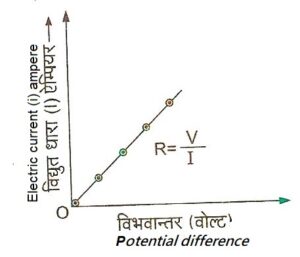
जो चालक इस नियम का पालन करते हैं, उन्हें ओमीय चालक कहा जाता है तथा जो चालक इस नियम का पालन नहीं करते, उन्हें अन-ओमीय चालक कहा जाता है। ओमीय चालकों के लिए V तथा I के बीच ग्राफ एक झुकी हुई सरल रेखा होती है, जबकि अन-ओमीय चालकों के लिए यह ग्राफ एक वक्र के रूप में होता है।ओमीय चालकों के लिए V तथा I के अनुपात को चालक का प्रतिरोध कहते हैं तथा इसे R से प्रदर्शित करते हैं।
V/I = R (नियतांक)
Ohm’s Law – According to Ohm’s law, “If the physical conditions of a conductor (such as the temperature of the material of the conductor etc.) remain unchanged, then the current flowing in the conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across the ends of the conductor.”
If the potential difference across the ends of a conductor is V and the current flowing in it is I, then
V/R = constant
The conductors which follow this rule are called Ohmic conductors and the conductors which do not follow this rule are called non-Ohmic conductors. For ohmic conductors, the graph between V and I is a bent straight line, whereas for non-ohmic conductors, this graph is in the form of a curve. For ohmic conductors, the ratio of V and I is called the resistance of the conductor. And it is represented by R.
V/I = R (constant)
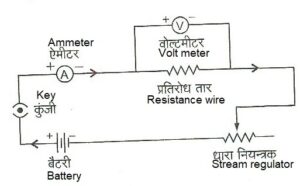
ओम के नियम का सत्यापन –
Verification of Ohm’s law –
ओम का नियम केवल धातु चालकों तथा मिश्रधातु-चालकों के लिए ही सत्य है। इस प्रयोग के लिए कॉन्स्टैण्टन, यूरेका अथवा मैंगनिन का एक प्रतिरोध तार लेते हैं और इसके श्रेणीक्रम में एक बैटरी, धारा-नियन्त्रक, ऐमीटर तथा कुंजी जोड़ देते हैं, जैसा की ऊपर चित्र में दिखाया गया है। एक वोल्टमीटर प्रतिरोध तार के सिरों के बीच जोड़ देते हैं।
Ohm’s law is true only for metallic conductors and alloy conductors. For this experiment, we take a resistance wire of Constantan, Eureka or Manganin and connect a battery, rheostat, ammeter and key in series, as shown in the figure above. A voltmeter is connected between the ends of the resistance wire.
परिपथ में कुंजी लगाते ही धारा बहने लगती है। धारा I का मान ऐमीटर से तथा प्रतिरोध के सिरों का विभवान्तर V वोल्टमीटर से पढ़ लेते हैं। अब धारा नियन्त्रक की सहायता से परिपथ में प्रवाहित धारा को बदल-बदल कर धारा I तथा विभवान्तर के मान पढ़ते जाते हैं और उन्हें एक सारणी में लिख लेते हैं। प्रत्येक प्रेक्षण से V और I का अनुपात समान प्राप्त होता है. जिससे ओम के नियम का सत्यापन हो जाता है। V तथा I के बीच ग्राफ खींचने पर, ग्राफ एक सरल रेखा के रूप में प्राप्त होता है जैसा की नीचे चित्र में दिखाया गया है। इस ग्राफ से भी ओम के नियम का सत्यापन हो जाता है।
As soon as the key is inserted in the circuit, current starts flowing. The value of current I is read from the ammeter and the potential difference V across the ends of the resistance is read from the voltmeter. Now with the help of current regulator, by changing the current flowing in the circuit, the values of current I and potential difference are read and write them in a table. The ratio of V and I is the same from each observation. Due to which Ohm’s law is verified. On drawing the graph between V and I, the graph is obtained in the form of a straight line as shown in the figure below. Ohm’s law is also verified from this graph.